Insights and Observations
Economic, Public Policy, and Fed Developments
- “You can think of this meeting as the talking-about-talking-about meeting, if you like,” noted Fed Chairman Jerome Powell on June 16th. He indicated the Fed’s assessment of the economic recovery had entered a new phase, and after months of “not even thinking about thinking about” tightening, the Fed had begun discussing under what conditions accommodation can be removed. The dot plot accompanying the release showed an acceleration of projected rate hikes, with a median projection of two by the end of 2023, up from none before 2024. Treasury yields fell on a decline in inflation expectations. Despite higher-than-expected transient inflation, the market appears to have faith the Fed is prepared to act to keep inflation in check. The Fed has emphasized a bullish economic forecast, and if the outlook were to deteriorate, so too would the likelihood of rate hikes. The Fed has signaled they will not tighten prematurely.
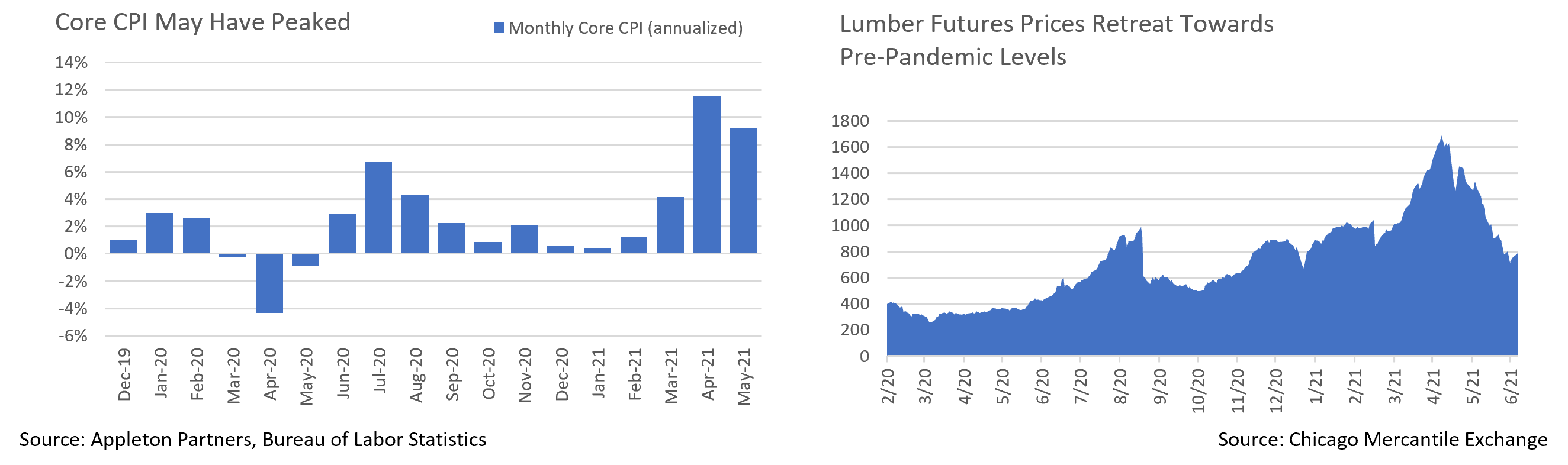
- Inflation exceeded expectations again in June with CPI surprising to the upside in June. Headline CPI hit 5%, the highest since 2008, with Core CPI’s 3.8% the highest reading since 1992. Gains were broad, although the largest contributions came from pandemic-impacted sectors. Used car prices, +7.3% for the month, were responsible for a third of the gain, with car rentals, household furnishings, airfares, and apparel also showing large increases. The final two are more reflation than inflation, and airfares remain below pre-pandemic highs. Airfares may contribute to inflation as they normalize but shouldn’t be a long-term inflation driver.
- Encouragingly, there are growing indications that recent inflation may have peaked. Anecdotal reports hold that carmaker chip shortages are easing; we expect confirmation in upcoming earnings calls. Lumber futures have fallen by nearly half since a peak earlier this year as mills roared back to meet demand. Durable Goods reports suggest the economy is starting to clear backlogs, with inventories increasing for a fourth straight month. Additionally, a Chinese crackdown on “commodity speculation” has led to price declines, easing input costs for manufacturers. And finally, periods with the worst of the “base effects” in year-over-year comparisons are now behind us, and month-over-month changes are accordingly starting to slow.
- Recent retail spending data supports this as well. While May’s sales release nominally showed a drop, it came after upward revisions to the March and April releases that collectively left absolute spending roughly in line with expectations. We noted last month that federal stimulus checks prompted a spending surge that was just beginning to abate; that surge appears to have been greater than initially estimated, and is now waning, though to still strong levels.
- Hiring also accelerated, with the June employment report posting an increase of 850k jobs vs. expectations of 720k. Most were in leisure and hospitality, where employment rose 343k, a sizeable gain although sector employment remains 15% lower than pre-pandemic levels. While there is concern that high demand for labor will pressure wages and in turn inflation, evidence is so far lacking. Wages rose 0.3% in June, due largely to a 1.0% increase in the low-paid leisure and hospitality sector. Increases in lower wage jobs in an economy that depends heavily on consumer spending are not necessarily an unwelcome development.
- There were two notable political developments in June. First, a bipartisan group of senators announced agreement on an 8-year infrastructure deal featuring $1.2 trillion in spending, including $579 billion of new money, although the proposal’s political future remains uncertain. Democratic Congressional leaders plan to bundle this with a larger “human infrastructure” bill passed via budget reconciliation, which Minority Leader McConnell has hinted is reason enough to kill the deal. Second, Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen announced the support of 130 OECD members for the Administration’s proposed 15% global minimum corporate tax bill. Again, celebration may be premature, as three of the nine holdouts – Estonia, Hungary, and Ireland – are EU members, and the EU requires unanimous consent of all members. If an agreement is reached it would slow corporate inversions and ease trade tensions in an increasingly globalized world.

Equity News and Notes
A Look at the Markets
- The stock market rallied on in June with the S&P 500 gaining 2.3% to raise its YTD total return to +15.3%. The Index closed a fifth consecutive month of gains at fresh all-time highs and has now posted five straight quarters of > 5% returns, a feat only matched in 1953-54.
- The prevailing bullish narrative that has driven the market to new highs remains in place. Global central bank liquidity, fiscal stimulus, economic reopening traction, positive corporate earnings, tight credit spreads, and an acceleration of corporate buybacks, dividend payments and M&A activity, have all provided tailwinds. Investors have reacted accordingly as evidenced by more than $350 billion of net equity ETF inflows during the 1H of 2021, more than any full year on record.
- Investor enthusiasm of this magnitude could represent a contrarian indicator though, as optimism may be running overly high. Market skeptics point to signs of peak economic and corporate earnings growth, waning Federal Reserve policy accommodation, and prospects of inflation, rising interest rates, and tax increases. Investors will need to accept a slower pace of growth, a condition that might forestall overheating and an adverse policy response. We are also watching stretched valuations. As we have often emphasized, valuation metrics provide little color on short-term returns, but they certainly narrow the margin for error.
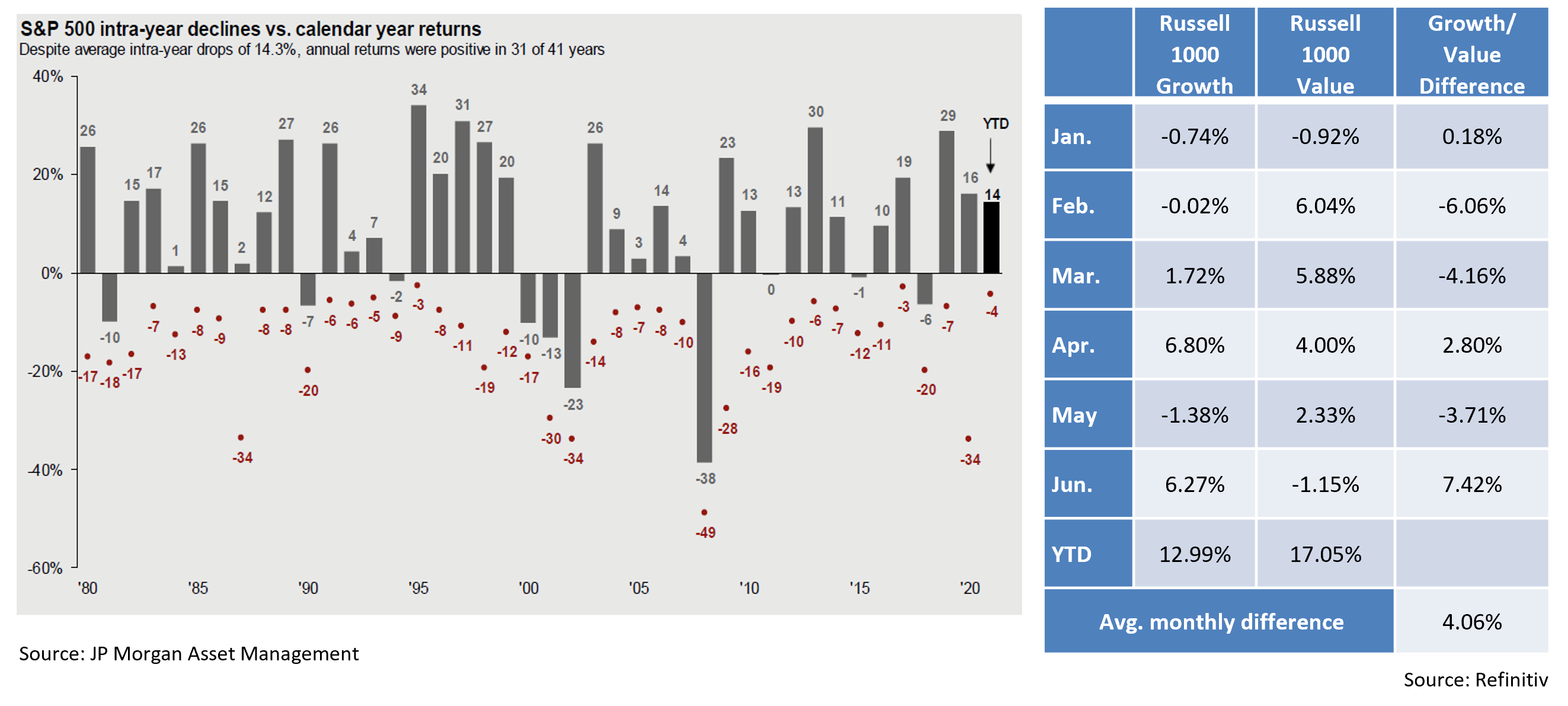
- Perhaps surprisingly, the strong performance of the S&P 500 has introduced minimal aggregate volatility. The Index traded with just a 0.62% average intraday range from peak to trough during June, the smallest margin since December 2019. The week heading into the July 4th holiday saw the weakest volume of the year, and the VIX (a widely followed volatility index) closed the quarter at 15, its lowest level since the start of the pandemic. We are only halfway through the year, but so far the S&P 500’s largest drawdown has been only -4%. We have no way of knowing if such muted downside will be sustained, although it is worth reminding investors that double-digit drawdowns are the norm, not an aberration.
- Despite relative calm at the surface, less visible style and sector rotations are evident. With investors seemingly more accepting of economic price volatility, embedded inflation expectations and bond yields dropped in June with the 10Yr UST yield falling by 20 bps to 1.40%. This helped the interest rate sensitive Technology sector gain nearly 7%, easily the strongest sector performance over that period. This resurgence fueled a sizeable gap in relative performance between Large Growth and Large Value given technology’s prominence within the growth camp. We expect further back and forth style swings as economic reopening, monetary policy, and interest rate dynamics play out. Timing these growth/value fluctuations is nearly impossible and being on the wrong side of such shifts can leave one whipsawed. We continue to employ a balanced approach to portfolio construction. While we generally favor growth-oriented stocks over the long-term and could see short-term outperformance should the rate of economic and earnings growth slow off recently surging levels that have benefited rebounding cyclicals, we intend to maintain some cyclical exposure in the face of upward pressure on interest rates.
From the Trading Desk
Municipal Markets
- A much awaited $1.2 trillion bipartisan infrastructure package was recently released, and the municipal markets are now engaged in debate over its likelihood of passage, as well as the merits of the package. The proposal calls for extensive transportation funding, impacting surface and public transportation, rail, airports, ports, and waterways. It also includes funding for energy, water infrastructure, and broadband. The proposal is to be funded by re-directing unused COVID relief money, increased IRS enforcement, and public-private partnerships rather than through higher corporate and individual taxes. Given that municipal performance often benefits from higher taxes, some anticipate a modestly adverse near-term market reaction. However, intense demand for municipals has not wavered, with almost $60 billion of YTD net mutual fund inflows along with 17 consecutive positive flow weeks. Regardless of how the infrastructure bill fares, we do not anticipate demand for municipals materially waning.
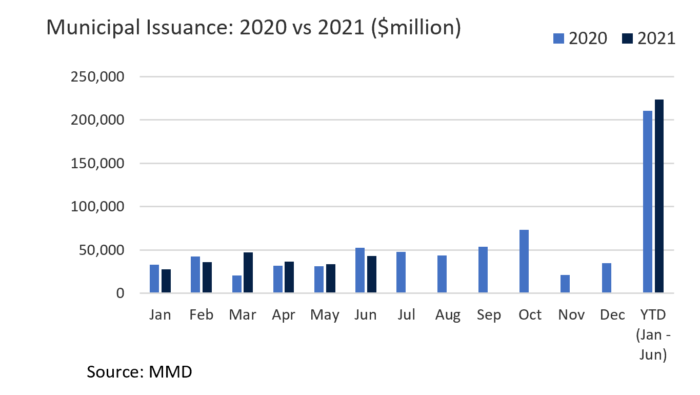
- On the flip side, passage of large-scale infrastructure should have a positive impact on bond supply. June issuance fell 17% short of the same month of 2020 and new supply will have to accelerate to meet 2021 projections. Federal support and a stronger economy have fostered much more favorable budget conditions than previously anticipated, slowing the need for issuers to come to market. Constrained net supply is supportive of bond prices but makes putting client assets to work challenging and we would welcome growth in tax-exempt supply that could be prompted by infrastructure development.
Corporate Bond Markets
- The Federal Reserve’s recently announced plans for a gradual unwind of the Pandemic Corporate Credit Facility portfolio was unsurprising in intent but surprising in its timing. At the time of the June 6th announcement the Fed held a $13.7 billion mix of corporate bond and ETF holdings, assets now expected to be liquidated by the end of the year. The Fed emphasized that “sales will be gradual and orderly and will aim to minimize the potential for any adverse impact on market functioning by taking into account daily liquidity.” Despite an acceleration in the process, market reaction was not noticeable, and we do not anticipate this action having a meaningful impact on the credit markets.
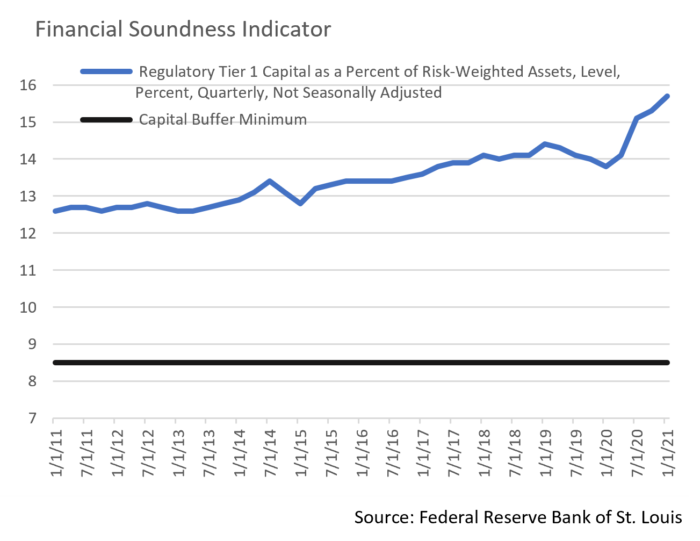
- In another positive development, the Federal Reserve released results of Dodd-Frank era bank stress tests on June 24th, the 3rd such test over the past 12 months. The results were reassuring as participating banks far exceeded risk-based minimum capital requirements under hypothetical scenarios that included a massive global recession adversely impacting the corporate debt markets and commercial real estate. Capital strength and stability not only reflects well on the broader corporate debt markets but, more specifically, allows banks to increase dividends and buy back stock. The six largest US banks can now do so up to $140 billion. Our outlook for large bank credits remains positive.
- Net Investment Grade Credit issuance in the first half of 2021 fell well short of 2020’s record setting pace yet remains comfortably ahead of 2019. June 2021’s $112.7 billion in new debt met market expectations and raised the YTD total to $796.3 billion. Although 2021 gross issuance is 32% behind 2020, it is running 34% ahead of 2019, an average year. Very low YTD new issue concessions (1.3 bps vs. 10.4 bps in 2020) demonstrate the strength of investor demand. Furthermore, we anticipate slowing issuance which would be a favorable technical for IG spreads.
- The resiliency of IG credit spreads has been evident throughout 2021 with trading confined within a narrow 20 bps band. June spreads opened with a move higher (+5 bps) as risk briefly appeared to be falling out of favor, although this quickly reversed. Bloomberg Barclays US IG Corporate Index closed June at +80 OAS, a tight level we have not seen since February 2005.
Financial Planning Perspectives
Pay Attention to Minor Details
With school out for summer vacation, it is a great time to discuss money management strategies with your children. Whether your kids are getting ready to head off to college for the first time or are still in high school and starting a summer job, several financial planning disciplines may be of value.
Appleton’s Upcoming Financial Planning Webinar
“What’s Driving Your Portfolio? Equity Analysis Concepts and Appleton’s Investment Process”
August 18th @ 4:00PM
For questions concerning our financial planning or wealth management services, please contact
Jim O’Neil, Managing Director, 617-338-0700 x775, [email protected]




